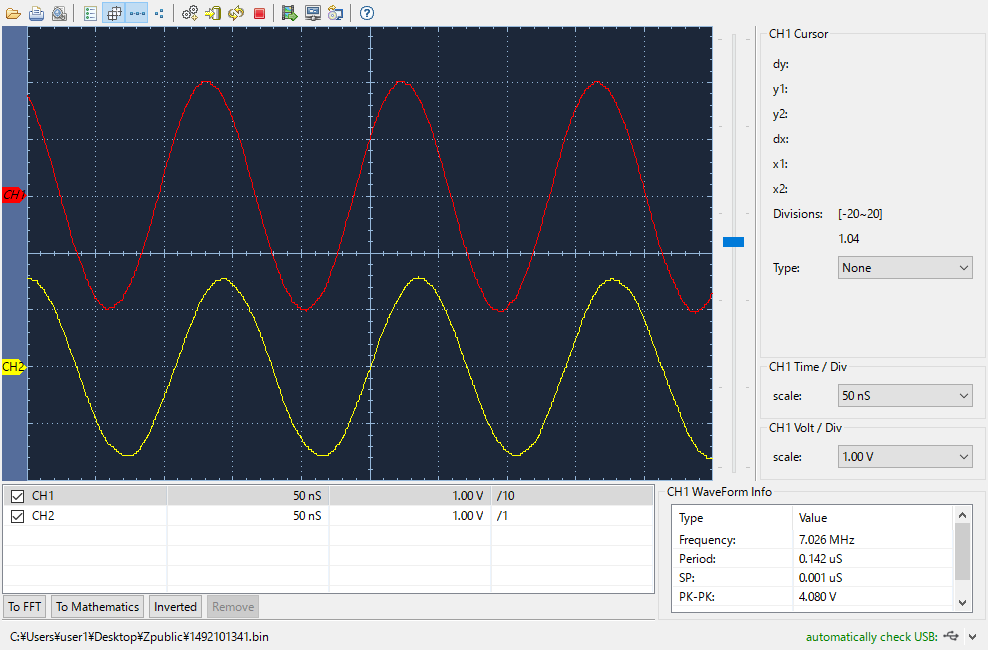
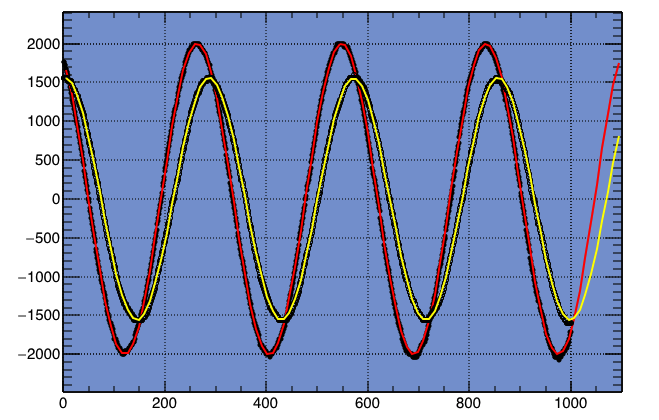
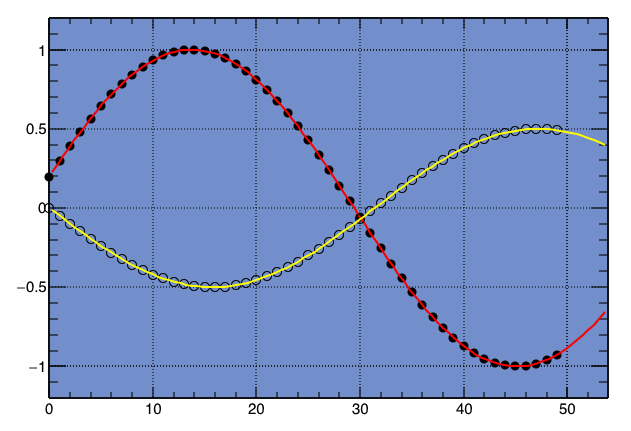
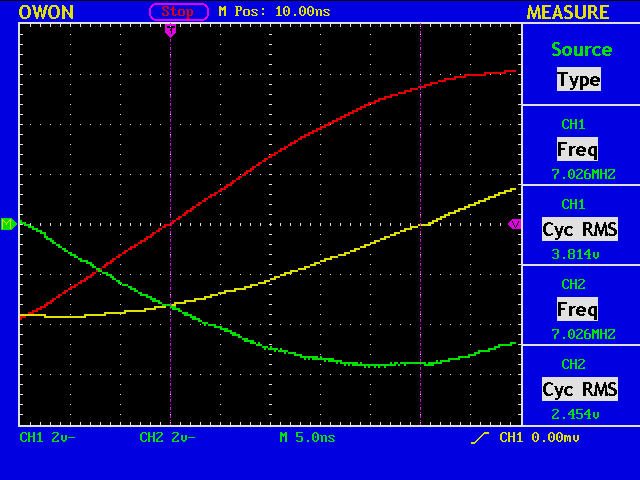
Now let’s try to measure the impedance of my dipole antenna. The figure shows the reference signal in red and the signal across the antenna in yellow. If the impedance of the dipole antenna is exactly 50 ohm, the two signals should be the same.
% head -15 owondata.txt
Save Time: 2016-09-11 13:27:26
Units:(mV)
CH1 CH2
Frequency: 7.026 MHz 7.042 MHz
Period: 0.142 uS 0.142 uS
SP: 0.001 uS 0.001 uS
PK-PK: 4.080 V 3.200 V
1 0.000 1760.00 1560.00
2 0.001 1760.00 1560.00
3 0.001 1720.00 1560.00
4 0.002 1720.00 1560.00
A text file obtained from the oscilloscope, OWON PDS 5022S, is fed into an AWK one-liner before being processed by a program written in ROOT.
% cat owondata.txt | awk 'NR>8 {print $1, $3}' >owondata_ch1.txt
% cat owondata.txt | awk 'NR>8 {print $1, $4}' >owondata_ch2.txt
// file name = mytest5.cc
{
TGraph *g = new TGraph("owondata_ch1.dat");
g->SetMarkerStyle( 20 );
g->SetMarkerSize( 0.5 );
g->Draw("AP");
TF1 *f1 = new TF1("f1", "[0]*sin([1]*x+[2])+[3]");
f1->SetParameter(0, 2000.0);
f1->SetParameter(1, 0.022);
f1->SetParameter(2, 0.0);
f1->SetParameter(3, 0.0);
f1->SetLineColor(kRed);
g->Fit(f1);
TGraph *h = new TGraph("owondata_ch2.dat");
h->SetMarkerStyle( 24 );
h->SetMarkerSize( 0.5 );
h->Draw("P");
TF1 *f2 = new TF1("f2", "[0]*sin([1]*x+[2])+[3]");
f2->SetParameter(0, 2000.0);
f2->SetParameter(1, 0.022);
f2->SetParameter(2, 0.0);
f2->SetParameter(3, 0.0);
f2->SetLineColor(kYellow);
h->Fit(f2);
}
% root mytest5.cc **************************************** Minimizer is Minuit / Migrad Chi2 = 536853 NDf = 996 Edm = 7.63442e-09 NCalls = 148 p0 = 2001.67 +/- 1.04511 p1 = 0.0220756 +/- 1.82267e-06 p2 = 2.03624 +/- 0.00102561 p3 = -12.2567 +/- 0.749788 **************************************** Minimizer is Minuit / Migrad Chi2 = 459226 NDf = 996 Edm = 8.91283e-08 NCalls = 128 p0 = 1558.13 +/- 0.960465 p1 = 0.0220847 +/- 2.15852e-06 p2 = 1.50439 +/- 0.00124773 p3 = -14.2113 +/- 0.68435
The parameters p0 and p2 are the amplitude and the phase, respectively, so the amplitude ratio is 1558.13/2001.67=0.778415, and the phase difference is 1.50439-2.03624=-0.531850[rad]=-30.4728[deg].