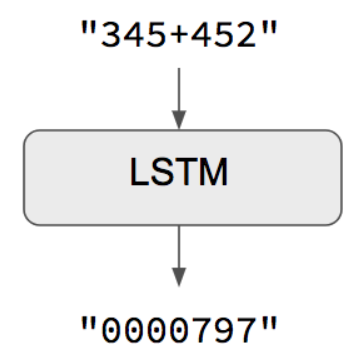
If you prefer to use an input sequence that better resembles a real-world situation, one way is to train with:
a, 101110
aa, 101110 101110
aal, 101110 101110 1011101010
aalii, 101110 101110 1011101010 1010 1010
(many lines deleted)
zythia, 111011101010 11101011101110 1110 10101010 1010 101110
zythum, 111011101010 11101011101110 1110 10101010 10101110 11101110
zyzomys, 111011101010 11101011101110 111011101010 111011101110 11101110 11101011101110 101010
zyzzogeton, 111011101010 11101011101110 111011101010 111011101010 111011101110 1110111010 10 1110 111011101110 111010
It is assumed that the inter-character space is perfectly recovered and is shown as a space character.
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= lstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 128) 67584 _________________________________________________________________ repeat_vector_1 (RepeatVecto (None, 4, 128) 0 _________________________________________________________________ lstm_2 (LSTM) (None, 4, 128) 131584 _________________________________________________________________ time_distributed_1 (TimeDist (None, 4, 27) 3483 ================================================================= Total params: 202,651 Trainable params: 202,651 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ Train on 4894 samples, validate on 100 samples
10111011101110 10101110 111010111010 1110101110 juck juck 1110101010 10101110 1011101010 1011101010 bull bull 101110111010 1010 1011101010 11101011101110 pily pily 1011101010 10101110 10 101010 lues laes 1110111010 111011101110 1011101110 111010 gown gown 10101010 101110 10101110 1011101010 haul haul 1110 111011101110 1010 1011101010 toil toil
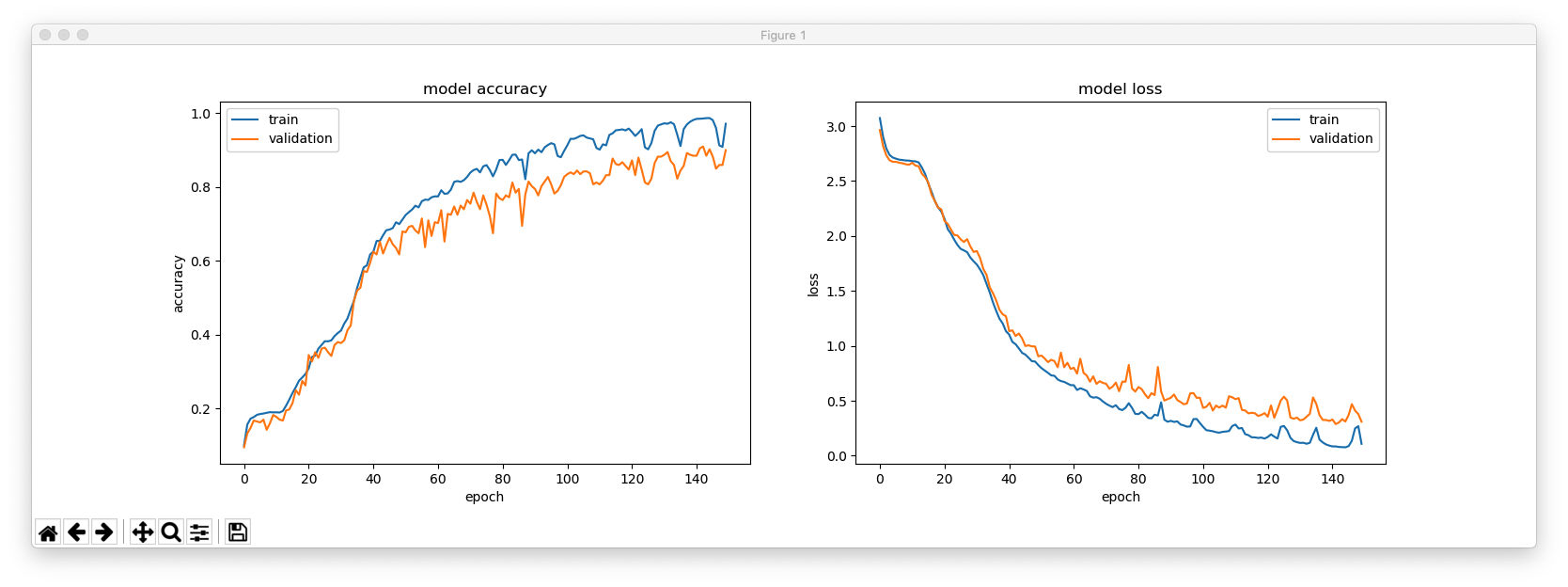
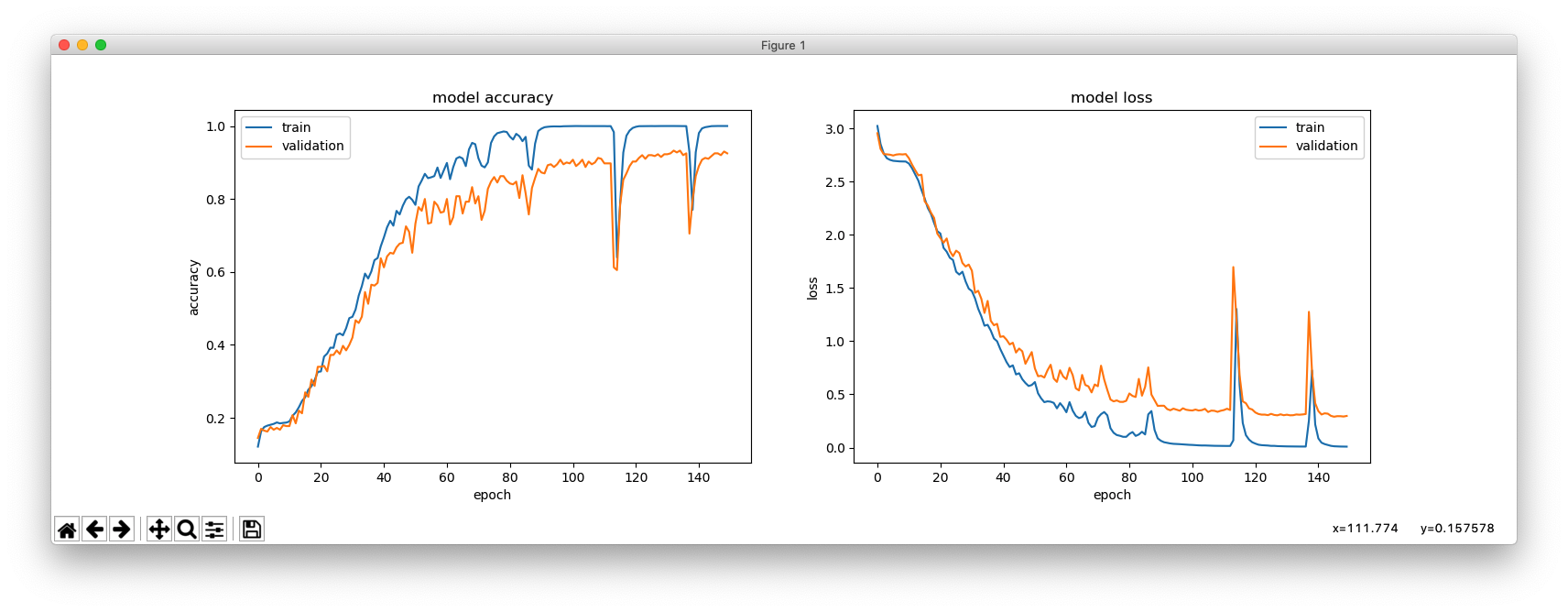
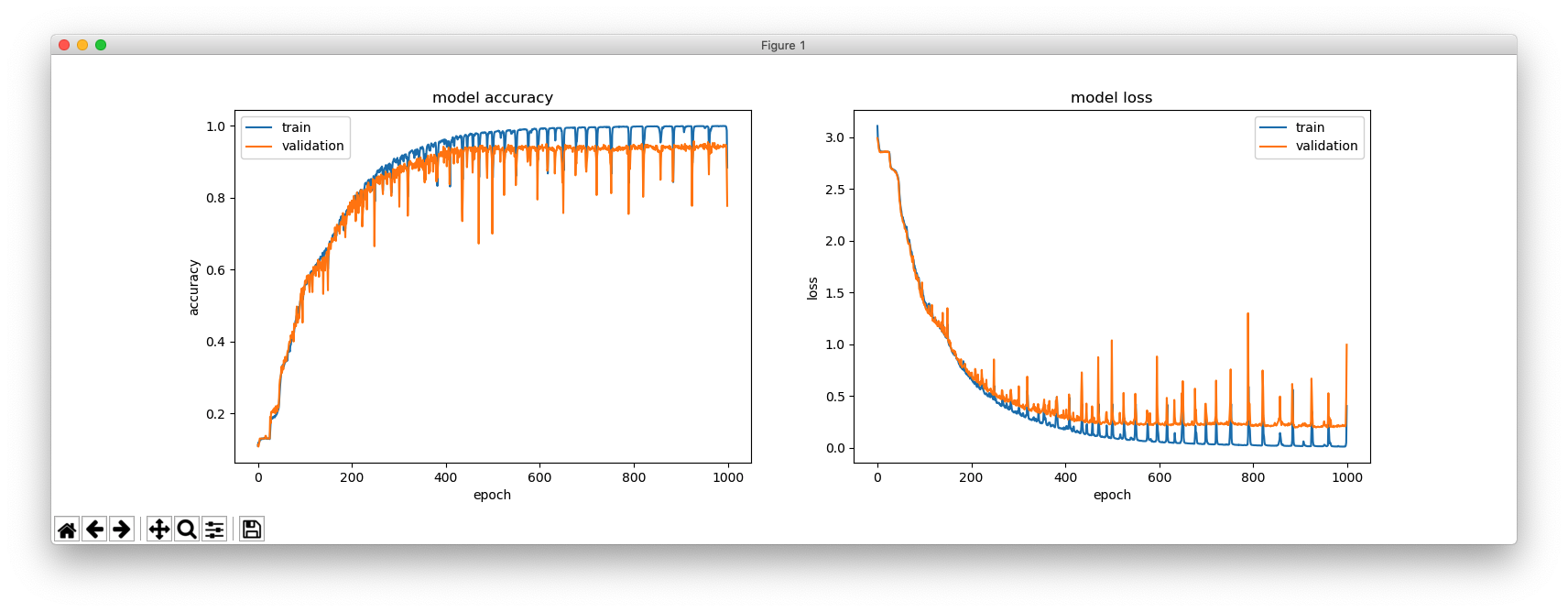
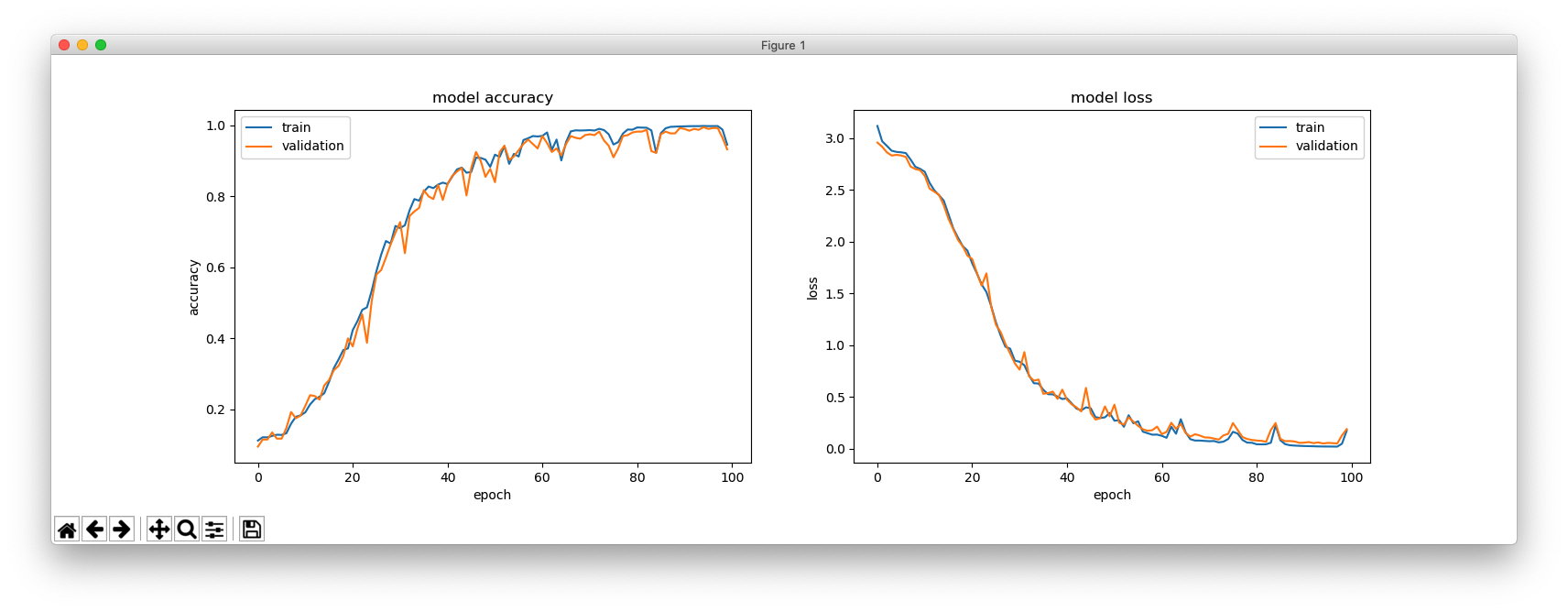
This is with hidden_size = 256.
This is with hidden_size = 64.
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= lstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 256) 266240 _________________________________________________________________ repeat_vector_1 (RepeatVecto (None, 4, 256) 0 _________________________________________________________________ lstm_2 (LSTM) (None, 4, 256) 525312 _________________________________________________________________ time_distributed_1 (TimeDist (None, 4, 27) 6939 ================================================================= Total params: 798,491 Trainable params: 798,491 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ Train on 4894 samples, validate on 100 samples
_________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= lstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 64) 17408 _________________________________________________________________ repeat_vector_1 (RepeatVecto (None, 4, 64) 0 _________________________________________________________________ lstm_2 (LSTM) (None, 4, 64) 33024 _________________________________________________________________ time_distributed_1 (TimeDist (None, 4, 27) 1755 ================================================================= Total params: 52,187 Trainable params: 52,187 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ Train on 4894 samples, validate on 100 samples
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras import layers
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class CharTable(object):
def __init__(self, chars):
self.chars = sorted(set(chars))
self.char_indices = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(self.chars))
self.indices_char = dict((i, c) for i, c in enumerate(self.chars))
def encode(self, token, num_rows):
x = np.zeros((num_rows, len(self.chars)))
for i, c in enumerate(token):
x[i, self.char_indices] = 1
return x
def decode(self, x, calc_argmax=True):
if calc_argmax:
x = [x.argmax(axis=-1)]
return ''.join(self.indices_char[int(v)] for v in x)
def main():
word_len = 4
max_len_x = 15 * word_len + (word_len - 1)
max_len_y = word_len
input_list = []
output_list = []
fin = 'words_morse10.txt'
with open(fin, 'r') as file:
for line in file.read().splitlines():
mylist = line.split(", ")
[word, morse] = mylist
morse = morse + ' ' * (max_len_x - len(morse))
if len(word) == word_len:
input_list.append(morse)
output_list.append(word)
chars_in = '10 '
chars_out = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz '
ctable_in = CharTable(chars_in)
ctable_out = CharTable(chars_out)
x = np.zeros((len(input_list), max_len_x, len(chars_in)))
y = np.zeros((len(output_list), max_len_y, len(chars_out)))
for i, token in enumerate(input_list):
x[i] = ctable_in.encode(token, max_len_x)
for i, token in enumerate(output_list):
y[i] = ctable_out.encode(token, max_len_y)
indices = np.arange(len(y))
np.random.shuffle(indices)
x = x[indices]
y = y[indices]
m = len(x) - 100
(x_train, x_val) = x[:m], x[m:]
(y_train, y_val) = y[:m], y[m:]
hidden_size = 128
batch_size = 128
nlayers = 1
epochs = 150
model = Sequential()
model.add(layers.LSTM(hidden_size, input_shape=(max_len_x, len(chars_in))))
model.add(layers.RepeatVector(word_len))
for _ in range(nlayers):
model.add(layers.LSTM(hidden_size, return_sequences=True))
model.add(layers.TimeDistributed(layers.Dense(len(chars_out), activation='softmax')))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
hist = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs, verbose=2, validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
predict = model.predict_classes(x_val)
for i in range(len(x_val)):
print("".join([ctable_in.decode(code) for code in x_val[i]]),
"".join([ctable_out.decode(code) for code in y_val[i]]), end=" ")
for j in range(word_len):
print(ctable_out.indices_char[predict[i][j]], end="")
print()
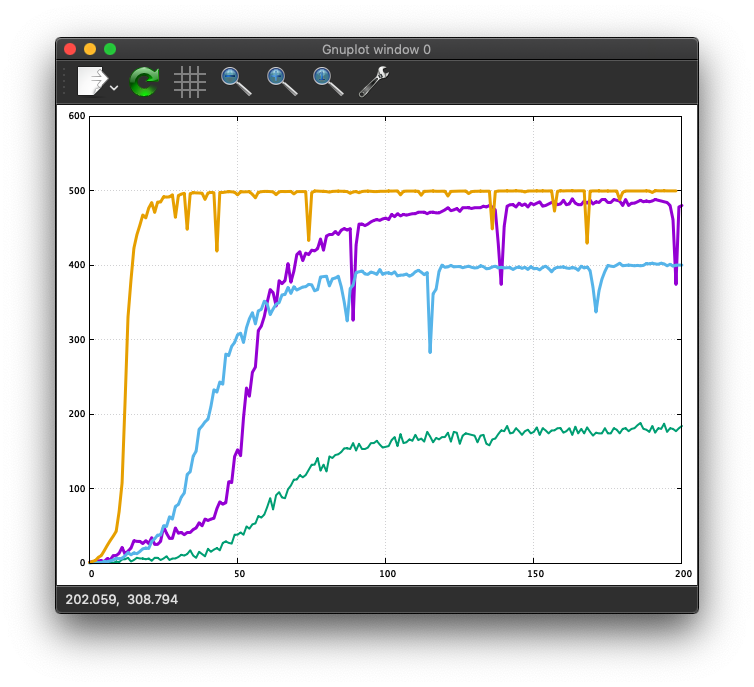
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(hist.history['acc'])
plt.plot(hist.history['val_acc'])
plt.title('model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(hist.history['loss'])
plt.plot(hist.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('model loss')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'validation'], loc='upper right')
plt.show()
main()
import numpy as np
def morse_encode(word):
return " ".join([morse_dict[i]for i in " ".join(word).split()])
def data_gen():
fin = 'words_alpha.txt'
with open(fin, 'r') as file:
for word in file.read().lower().splitlines():
print(word, morse_encode(word), sep=", ")
return
alphabet = list("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz")
# values = ['.-', '-...', '-.-.', '-..', '.', '..-.', '--.', '....', '..', '.---', '-.-',
# '.-..', '--', '-.', '---', '.--.', '--.-',
# '.-.', '...', '-', '..-', '...-', '.--', '-..-', '-.--', '--..']
values = ['101110', '1110101010', '111010111010', '11101010', '10', '1010111010',
'1110111010', '10101010', '1010', '10111011101110', '1110101110',
'1011101010', '11101110', '111010', '111011101110', '101110111010',
'11101110101110', '10111010', '101010', '1110', '10101110', '1010101110',
'1011101110', '111010101110', '11101011101110', '111011101010']
morse_dict = dict(zip(alphabet, values))
data_gen()