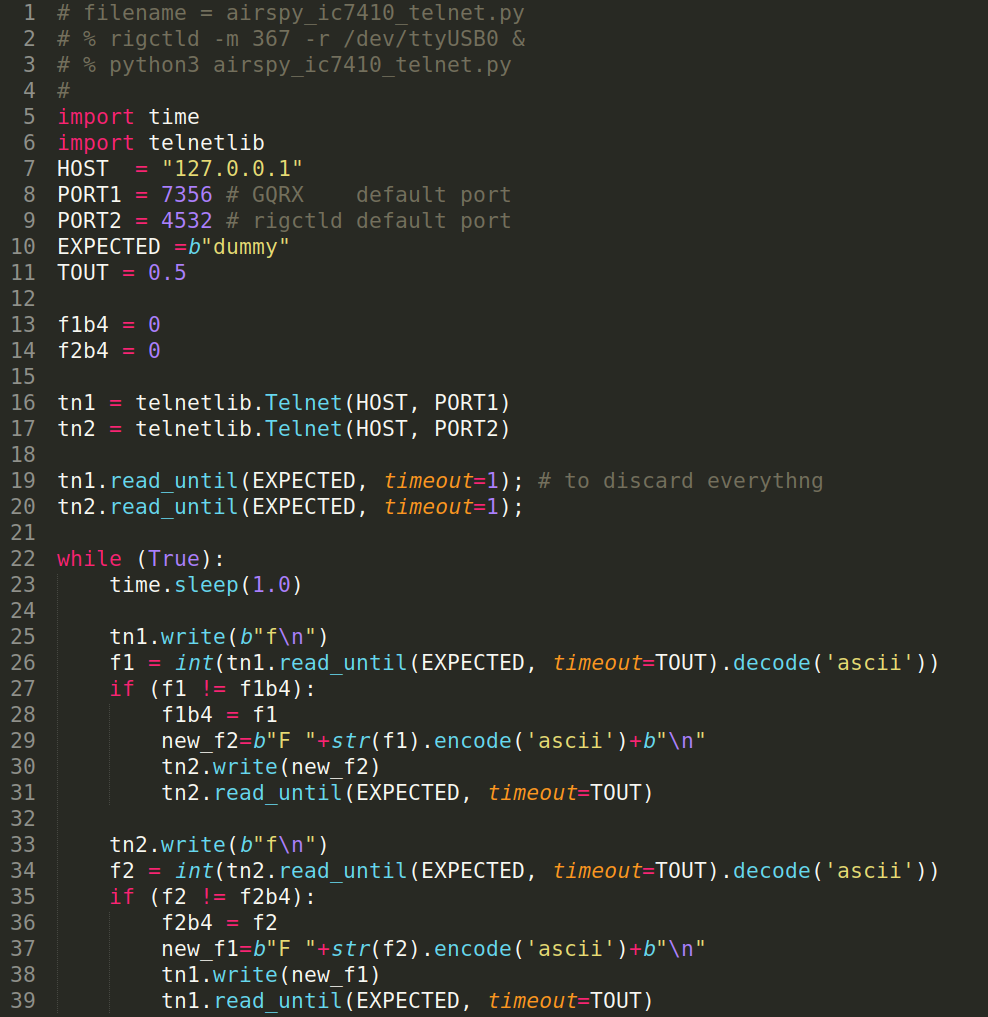
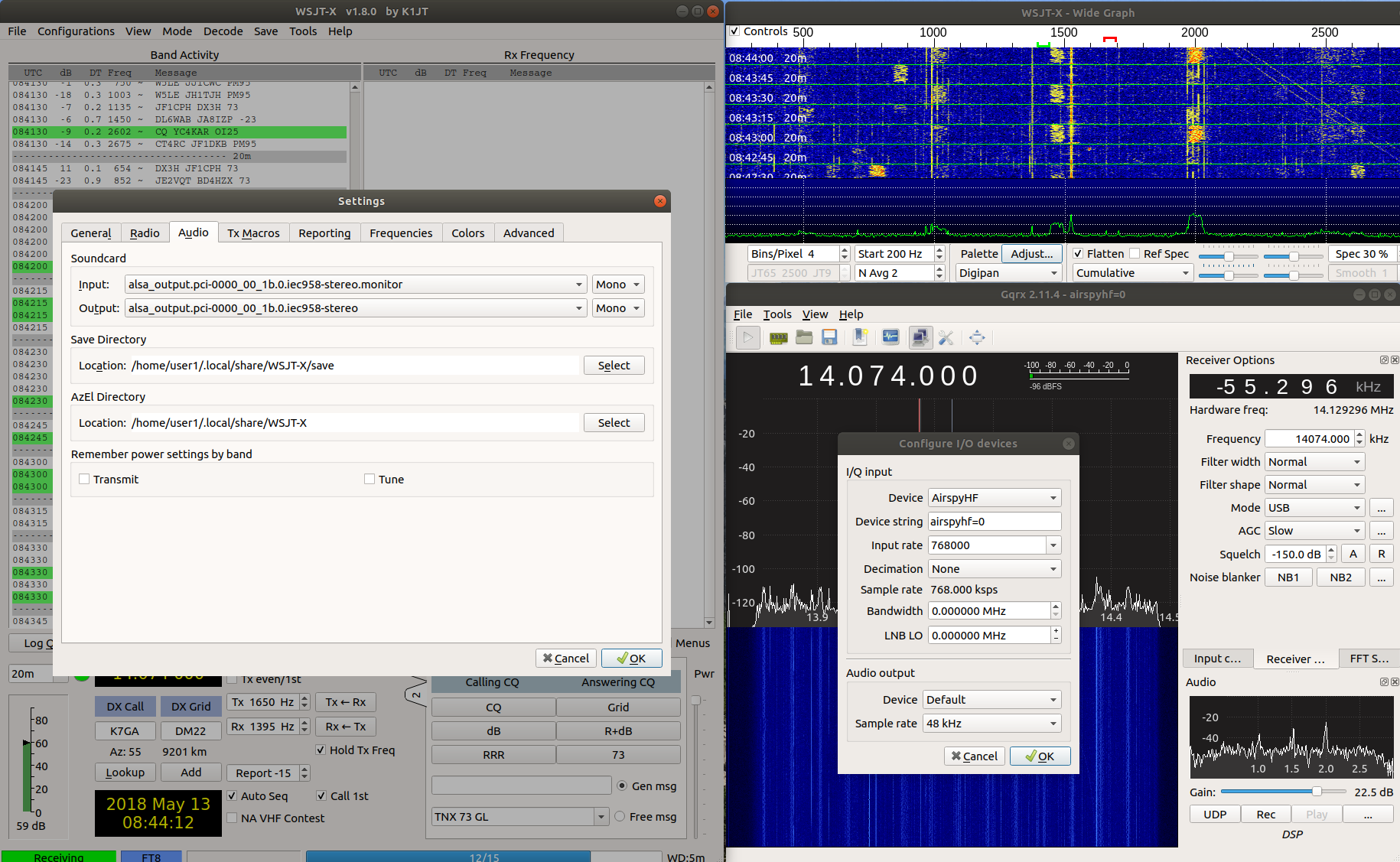
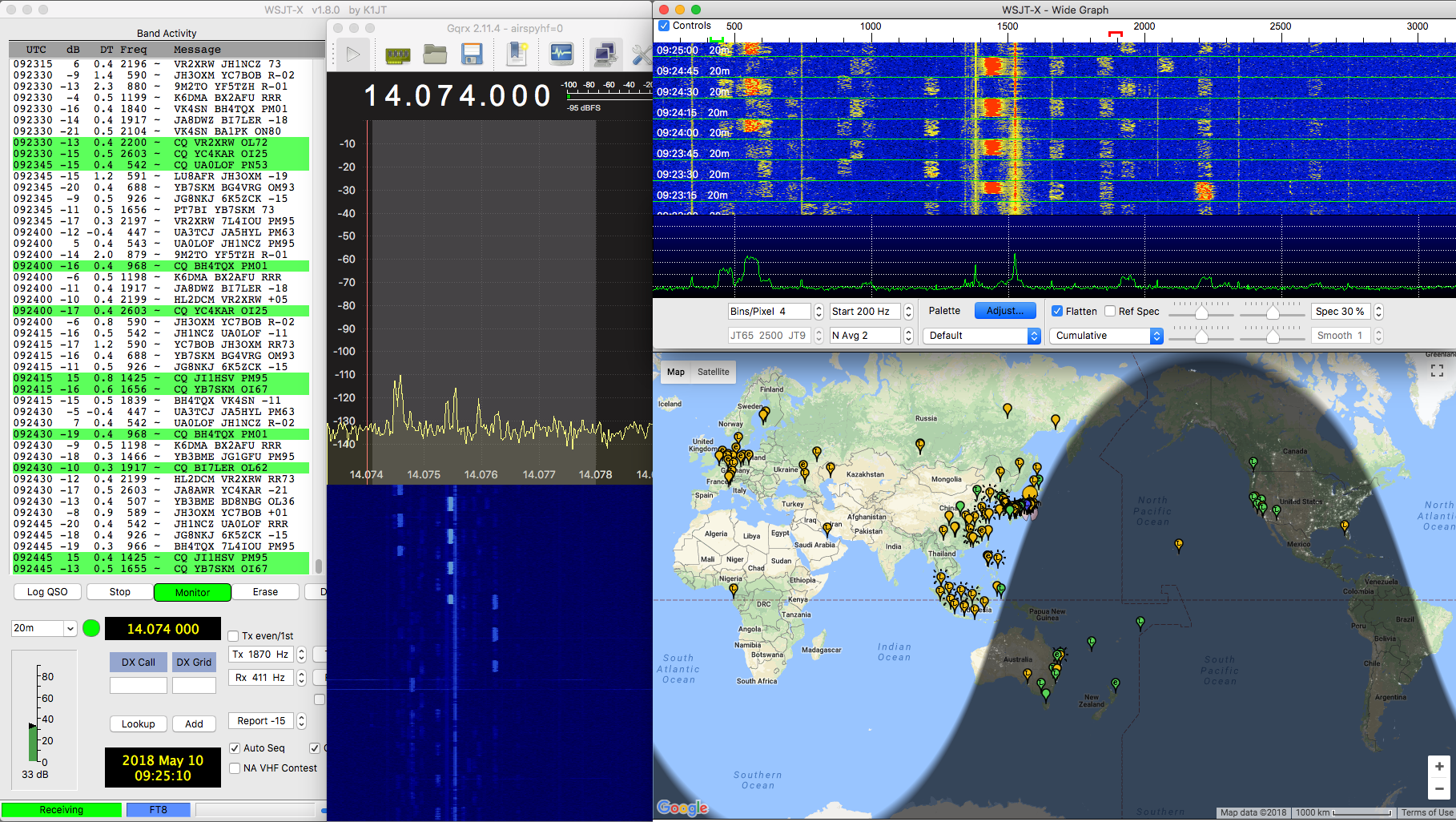
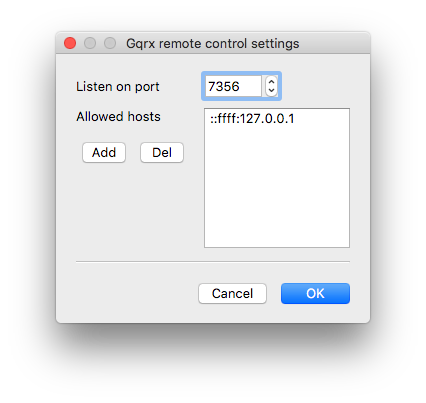
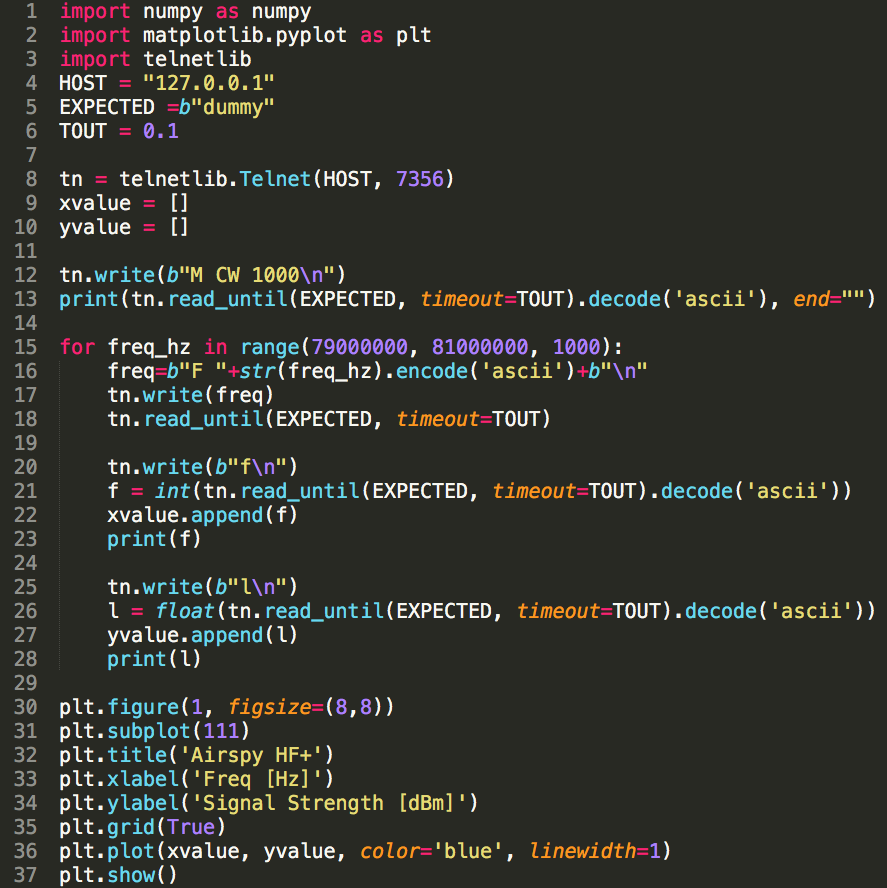
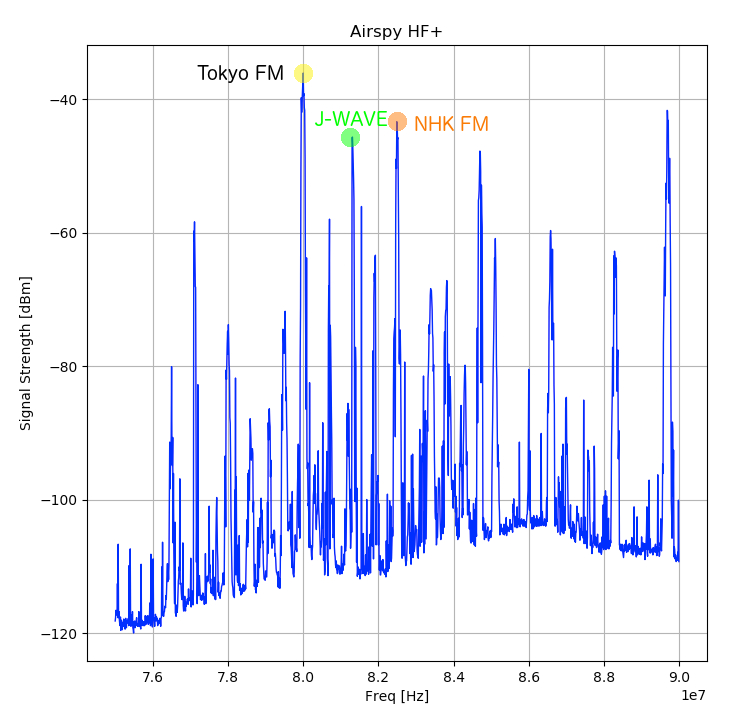
When you use both HF+ and IC-7410, it would be convenient if the two frequencies are in sync across the equipment.
There could be various ways to realize that, and here is one:
# filename = airspy_ic7410_telnet.py
# % rigctld -m 367 -r /dev/ttyUSB0 &
# % python3 airspy_ic7410_telnet.py
#
import time
import telnetlib
HOST = "127.0.0.1"
PORT1 = 7356 # GQRX default port
PORT2 = 4532 # rigctld default port
EXPECTED =b"dummy"
TOUT = 0.5
f1b4 = 0
f2b4 = 0
tn1 = telnetlib.Telnet(HOST, PORT1)
tn2 = telnetlib.Telnet(HOST, PORT2)
tn1.read_until(EXPECTED, timeout=1); # to discard everythng
tn2.read_until(EXPECTED, timeout=1);
while (True):
time.sleep(1.0)
tn1.write(b"f\n")
f1 = int(tn1.read_until(EXPECTED, timeout=TOUT).decode('ascii'))
if (f1 != f1b4):
f1b4 = f1
new_f2=b"F "+str(f1).encode('ascii')+b"\n"
tn2.write(new_f2)
tn2.read_until(EXPECTED, timeout=TOUT)
tn2.write(b"f\n")
f2 = int(tn2.read_until(EXPECTED, timeout=TOUT).decode('ascii'))
if (f2 != f2b4):
f2b4 = f2
new_f1=b"F "+str(f2).encode('ascii')+b"\n"
tn1.write(new_f1)
tn1.read_until(EXPECTED, timeout=TOUT)
This small program uses telnet to talk to HF+ (via Gqrx) and to IC-7410 (via rigctld).