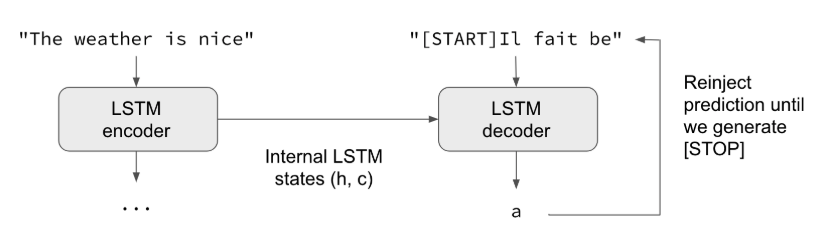
これは、Kerasのサンプルコードです。英語の文を仏語に翻訳します。
英語と仏語の文のペアを用いて、モデルをトレーニングします。
Is she Japanese? Est-elle japonaise ? Is she a doctor? Est-elle médecin ?
私のMac miniで1時間ほどすると、このような結果が得られます。
Input sentence: Be nice. Decoded sentence: Soyez gentil ! - Input sentence: Drop it! Decoded sentence: Laissez tomber ! - Input sentence: Get out! Decoded sentence: Sortez !
ここまでは、良いですね。しかしながら、私たちが本当に知りたいのは、以下のようなトレーニング系列を与えた時に何が起きるかです。
a, .-
aa, .- .-
aal, .- .- .-..
aalii, .- .- .-.. .. ..
(many lines deleted)
antidivorce, .- -. - .. -.. .. ...- --- .-. -.-. .
antidogmatic, .- -. - .. -.. --- --. -- .- - .. -.-.
antidomestic, .- -. - .. -.. --- -- . ... - .. -.-.
antidominican, .- -. - .. -.. --- -- .. -. .. -.-. .- -.
しばらく時間が経過したのち(トレーニング系列のサイズによりますが)、このようになります。
Number of samples: 10000 Number of unique input tokens: 26 Number of unique output tokens: 5 Max sequence length for inputs: 23 Max sequence length for outputs: 95 Train on 8000 samples, validate on 2000 samples Epoch 1/100 - Input sentence: abbacy Decoded sentence: .- -... -... .- -.-. -.-- - Input sentence: abbadide Decoded sentence: .- -... -... .- -.. .. -.. . - Input sentence: abbas Decoded sentence: .- -... -... .- ... Process finished with exit code 0
この特定の例では、トレーニング系列に含まれるサンプルをデコードしていることに留意してください。
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, LSTM, Dense
import numpy as np
batch_size = 64 # Batch size for training.
epochs = 100 # Number of epochs to train for.
latent_dim = 256 # Latent dimensionality of the encoding space.
num_samples = 10000 # Number of samples to train on.
# num_samples = 5
data_path = 'seq2seq.txt'
data_path = 'words_morse.txt'
# Vectorize the data.
input_texts = []
target_texts = []
input_characters = set()
target_characters = set()
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.read().split('\n')
for line in lines[: min(num_samples, len(lines) - 1)]:
# input_text, target_text = line.split('\t')
input_text, target_text = line.split(', ')
print("input_text [", input_text, "]", sep="")
print("target_text [", target_text, "]", sep="")
# We use "tab" as the "start sequence" character
# for the targets, and "\n" as "end sequence" character.
target_text = '\t' + target_text + '\n'
input_texts.append(input_text)
target_texts.append(target_text)
for char in input_text:
if char not in input_characters:
input_characters.add(char)
for char in target_text:
if char not in target_characters:
target_characters.add(char)
input_characters = sorted(list(input_characters))
target_characters = sorted(list(target_characters))
num_encoder_tokens = len(input_characters)
num_decoder_tokens = len(target_characters)
max_encoder_seq_length = max([len(txt) for txt in input_texts])
max_decoder_seq_length = max([len(txt) for txt in target_texts])
print('Number of samples:', len(input_texts))
print('Number of unique input tokens:', num_encoder_tokens)
print('Number of unique output tokens:', num_decoder_tokens)
print('Max sequence length for inputs:', max_encoder_seq_length)
print('Max sequence length for outputs:', max_decoder_seq_length)
input_token_index = dict(
[(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(input_characters)])
target_token_index = dict(
[(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(target_characters)])
encoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(len(input_texts), max_encoder_seq_length, num_encoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
decoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(len(input_texts), max_decoder_seq_length, num_decoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
decoder_target_data = np.zeros(
(len(input_texts), max_decoder_seq_length, num_decoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
for i, (input_text, target_text) in enumerate(zip(input_texts, target_texts)):
for t, char in enumerate(input_text):
encoder_input_data[i, t, input_token_index[char]] = 1.
for t, char in enumerate(target_text):
# decoder_target_data is ahead of decoder_input_data by one timestep
decoder_input_data[i, t, target_token_index[char]] = 1.
if t > 0:
# decoder_target_data will be ahead by one timestep
# and will not include the start character.
decoder_target_data[i, t - 1, target_token_index[char]] = 1.
# Define an input sequence and process it.
encoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None, num_encoder_tokens))
encoder = LSTM(latent_dim, return_state=True)
encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = encoder(encoder_inputs)
# We discard `encoder_outputs` and only keep the states.
encoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
# Set up the decoder, using `encoder_states` as initial state.
decoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None, num_decoder_tokens))
# We set up our decoder to return full output sequences,
# and to return internal states as well. We don't use the
# return states in the training model, but we will use them in inference.
decoder_lstm = LSTM(latent_dim, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder_lstm(decoder_inputs,
initial_state=encoder_states)
decoder_dense = Dense(num_decoder_tokens, activation='softmax')
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)
# Define the model that will turn
# `encoder_input_data` & `decoder_input_data` into `decoder_target_data`
model = Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], decoder_outputs)
# Run training
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy')
model.fit([encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data], decoder_target_data,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_split=0.2)
# Save model
model.save('s2s.h5')
# Next: inference mode (sampling).
# Here's the drill:
# 1) encode input and retrieve initial decoder state
# 2) run one step of decoder with this initial state
# and a "start of sequence" token as target.
# Output will be the next target token
# 3) Repeat with the current target token and current states
# Define sampling models
encoder_model = Model(encoder_inputs, encoder_states)
decoder_state_input_h = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_state_input_c = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_states_inputs = [decoder_state_input_h, decoder_state_input_c]
decoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = decoder_lstm(
decoder_inputs, initial_state=decoder_states_inputs)
decoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)
decoder_model = Model(
[decoder_inputs] + decoder_states_inputs,
[decoder_outputs] + decoder_states)
# Reverse-lookup token index to decode sequences back to
# something readable.
reverse_input_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in input_token_index.items())
reverse_target_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in target_token_index.items())
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# Encode the input as state vectors.
states_value = encoder_model.predict(input_seq)
# Generate empty target sequence of length 1.
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
# Populate the first character of target sequence with the start character.
target_seq[0, 0, target_token_index['\t']] = 1.
# Sampling loop for a batch of sequences
# (to simplify, here we assume a batch of size 1).
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
while not stop_condition:
output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict(
[target_seq] + states_value)
# Sample a token
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
sampled_char = reverse_target_char_index[sampled_token_index]
decoded_sentence += sampled_char
# Exit condition: either hit max length
# or find stop character.
if (sampled_char == '\n' or
len(decoded_sentence) > max_decoder_seq_length):
stop_condition = True
# Update the target sequence (of length 1).
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
target_seq[0, 0, sampled_token_index] = 1.
# Update states
states_value = [h, c]
return decoded_sentence
def main():
for seq_index in range(100):
# Take one sequence (part of the training set)
# for trying out decoding.
input_seq = encoder_input_data[seq_index: seq_index + 1]
decoded_sentence = decode_sequence(input_seq)
print('-')
print('Input sentence:', input_texts[seq_index])
print('Decoded sentence:', decoded_sentence)
main()