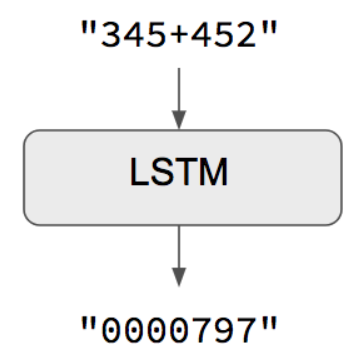
1つの簡単な例はこれです:
https://keras.io/examples/addition_rnn/
https://blog.keras.io/a-ten-minute-introduction-to-sequence-to-sequence-learning-in-keras.html
LSTMは、Long short-term memoryの略で、recurrent neural network (RNN)の一種です。
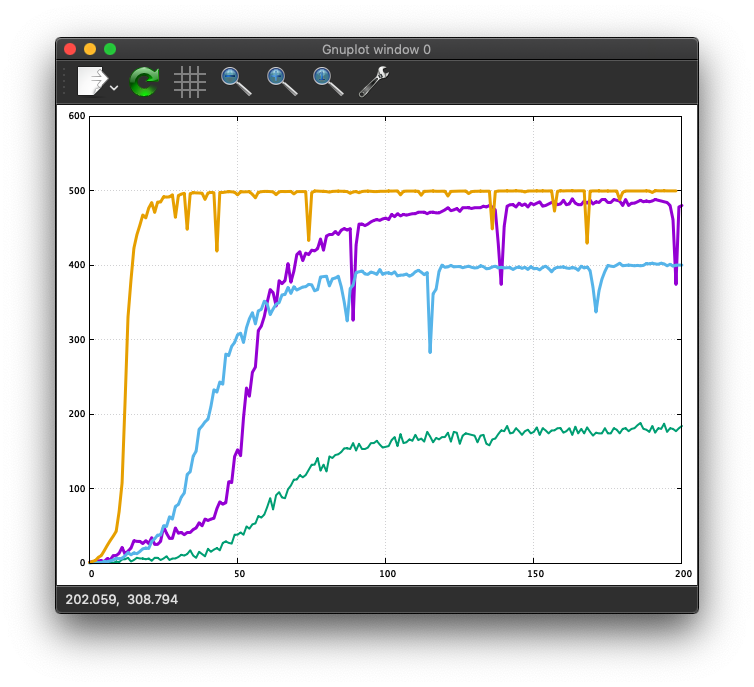
ハイパーパラメータを変えて、いくつかの学習曲線が図に示されています。
当然のことながら、予測は完璧ではありません。
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras import layers
import numpy as np
from six.moves import range
class CharacterTable(object):
"""Given a set of characters:
+ Encode them to a one-hot integer representation
+ Decode the one-hot or integer representation to their character output
+ Decode a vector of probabilities to their character output
"""
def __init__(self, chars):
"""Initialize character table.
# Arguments
chars: Characters that can appear in the input.
"""
self.chars = sorted(set(chars))
self.char_indices = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(self.chars))
self.indices_char = dict((i, c) for i, c in enumerate(self.chars))
def encode(self, C, num_rows):
"""One-hot encode given string C.
# Arguments
C: string, to be encoded.
num_rows: Number of rows in the returned one-hot encoding. This is
used to keep the # of rows for each data the same.
"""
x = np.zeros((num_rows, len(self.chars)))
for i, c in enumerate(C):
x[i, self.char_indices] = 1
return x
def decode(self, x, calc_argmax=True):
"""Decode the given vector or 2D array to their character output.
# Arguments
x: A vector or a 2D array of probabilities or one-hot representations;
or a vector of character indices (used with `calc_argmax=False`).
calc_argmax: Whether to find the character index with maximum
probability, defaults to `True`.
"""
if calc_argmax:
x = x.argmax(axis=-1)
return ''.join(self.indices_char[x] for x in x)
class colors:
ok = '\033[92m'
fail = '\033[91m'
close = '\033[0m'
# Parameters for the model and dataset.
TRAINING_SIZE = 50000
DIGITS = 3
REVERSE = True
# Maximum length of input is 'int + int' (e.g., '345+678'). Maximum length of
# int is DIGITS.
MAXLEN = DIGITS + 1 + DIGITS
# All the numbers, plus sign and space for padding.
chars = '0123456789+ '
ctable = CharacterTable(chars)
questions = []
expected = []
seen = set()
print('Generating data...')
while len(questions) < TRAINING_SIZE:
f = lambda: int(''.join(np.random.choice(list('0123456789'))
for i in range(np.random.randint(1, DIGITS + 1))))
a, b = f(), f()
# Skip any addition questions we've already seen
# Also skip any such that x+Y == Y+x (hence the sorting).
key = tuple(sorted((a, b)))
if key in seen:
continue
seen.add(key)
# Pad the data with spaces such that it is always MAXLEN.
q = '{}+{}'.format(a, b)
query = q + ' ' * (MAXLEN - len(q))
ans = str(a + b)
# Answers can be of maximum size DIGITS + 1.
ans += ' ' * (DIGITS + 1 - len(ans))
if REVERSE:
# Reverse the query, e.g., '12+345 ' becomes ' 543+21'. (Note the
# space used for padding.)
query = query[::-1]
questions.append(query)
expected.append(ans)
print('Total addition questions:', len(questions))
print('Vectorization...')
x = np.zeros((len(questions), MAXLEN, len(chars)), dtype=np.bool)
y = np.zeros((len(questions), DIGITS + 1, len(chars)), dtype=np.bool)
for i, sentence in enumerate(questions):
x[i] = ctable.encode(sentence, MAXLEN)
for i, sentence in enumerate(expected):
y[i] = ctable.encode(sentence, DIGITS + 1)
# Shuffle (x, y) in unison as the later parts of x will almost all be larger
# digits.
indices = np.arange(len(y))
np.random.shuffle(indices)
x = x[indices]
y = y[indices]
# Explicitly set apart 10% for validation data that we never train over.
split_at = len(x) - len(x) // 10
(x_train, x_val) = x[:split_at], x[split_at:]
(y_train, y_val) = y[:split_at], y[split_at:]
print('Training Data:')
print(x_train.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
print('Validation Data:')
print(x_val.shape)
print(y_val.shape)
# Try replacing GRU, or SimpleRNN.
RNN = layers.LSTM
HIDDEN_SIZE = 128
BATCH_SIZE = 128
LAYERS = 1
print('Build model...')
model = Sequential()
# "Encode" the input sequence using an RNN, producing an output of HIDDEN_SIZE.
# Note: In a situation where your input sequences have a variable length,
# use input_shape=(None, num_feature).
model.add(RNN(HIDDEN_SIZE, input_shape=(MAXLEN, len(chars))))
# As the decoder RNN's input, repeatedly provide with the last output of
# RNN for each time step. Repeat 'DIGITS + 1' times as that's the maximum
# length of output, e.g., when DIGITS=3, max output is 999+999=1998.
model.add(layers.RepeatVector(DIGITS + 1))
# The decoder RNN could be multiple layers stacked or a single layer.
for _ in range(LAYERS):
# By setting return_sequences to True, return not only the last output but
# all the outputs so far in the form of (num_samples, timesteps,
# output_dim). This is necessary as TimeDistributed in the below expects
# the first dimension to be the timesteps.
model.add(RNN(HIDDEN_SIZE, return_sequences=True))
# Apply a dense layer to the every temporal slice of an input. For each of step
# of the output sequence, decide which character should be chosen.
model.add(layers.TimeDistributed(layers.Dense(len(chars), activation='softmax')))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
# Train the model each generation and show predictions against the validation
# dataset.
for iteration in range(1, 200):
correct_count = 0
error_count = 0
print()
print('- ' * 50)
print('Iteration', iteration)
model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
epochs=1,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
# Select 10 samples from the validation set at random so we can visualize
# errors.
for i in range(len(x_val)):
rowx, rowy = x_val[np.array([i])], y_val[np.array([i])]
preds = model.predict_classes(rowx, verbose=0)
q = ctable.decode(rowx[0])
correct = ctable.decode(rowy[0])
guess = ctable.decode(preds[0], calc_argmax=False)
print('Q', q[::-1] if REVERSE else q, end=' ')
print('T', correct, end=' ')
if correct == guess:
print(colors.ok + '☑' + colors.close, end=' ')
correct_count = correct_count + 1
else:
print(colors.fail + '☒' + colors.close, end=' ')
error_count = error_count + 1
print(guess)
print("score = ", correct_count / (correct_count+error_count))